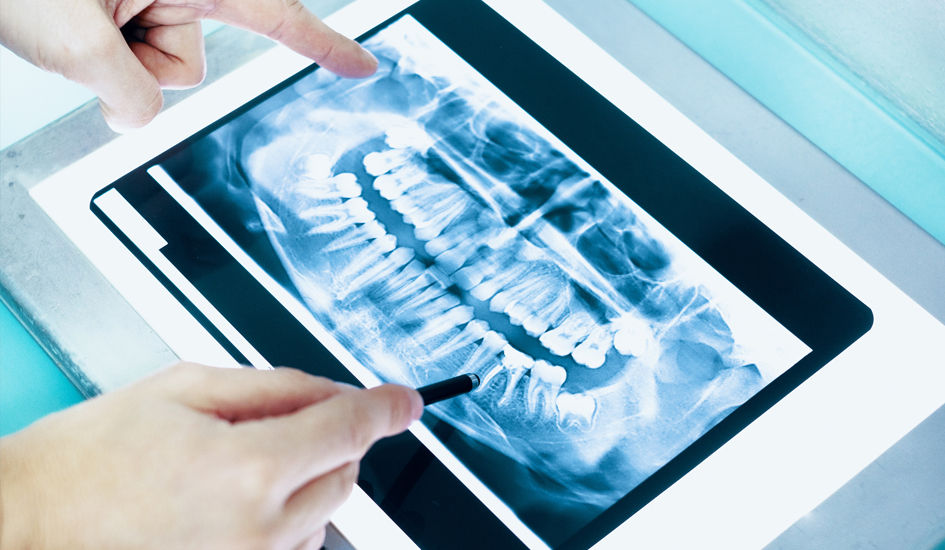
Dental X-rays are an essential part of modern dentistry, offering crucial insights into a patient’s oral health that can’t be detected with a visual examination alone. While some may hesitate about undergoing X-rays due to concerns about radiation exposure or cost, understanding the role and importance of X-rays in dental diagnostics can help clarify why …
Dental X-rays are an essential part of modern dentistry, offering crucial insights into a patient’s oral health that can’t be detected with a visual examination alone. While some may hesitate about undergoing X-rays due to concerns about radiation exposure or cost, understanding the role and importance of X-rays in dental diagnostics can help clarify why they are a necessary tool for maintaining long-term oral health. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of dental X-rays, their benefits, safety considerations, and the vital role they play in diagnosing and preventing a wide range of dental issues.
Why Are X-Rays Essential in Dentistry?
X-rays, also known as radiographs, allow dentists to see beneath the surface of the teeth and gums. A regular dental exam can only reveal issues that are visible above the gum line, but many dental problems start deep within the tooth or jawbone and are not noticeable in their early stages. Dental X-rays provide images that help dentists detect and diagnose these hidden issues, allowing for more effective treatment and prevention.
Key Reasons Why X-Rays Are Important:
- Early Detection of Cavities and Decay: Cavities often develop between the teeth or beneath fillings where they are not visible during a visual exam. X-rays allow dentists to detect tooth decay at its earliest stages, enabling early treatment and preventing it from spreading.
- Identification of Bone Loss and Gum Disease: X-rays help dentists assess the health of the bone supporting the teeth. If bone loss is detected, it’s often an early sign of periodontal (gum) disease, which can lead to tooth loss if untreated.
- Monitoring Dental Development in Children: For children, X-rays are essential to monitor the growth and alignment of teeth, particularly as permanent teeth emerge. Dentists can use X-rays to identify potential alignment issues, crowded teeth, or impacted teeth and recommend preventive treatments.
- Detection of Oral Infections or Abscesses: Dental infections, especially those that occur deep within the gums or jawbone, are not always visible or painful at first. X-rays can reveal the presence of infections, abscesses, or cysts, allowing dentists to provide prompt treatment.
- Assessment of Tooth and Jawbone Structure: Dental X-rays give dentists a comprehensive view of the tooth roots, jawbone structure, and surrounding tissues. This is especially helpful for planning procedures like extractions, root canals, and dental implants, where detailed knowledge of the tooth’s structure is crucial.
Types of Dental X-Rays
There are several types of dental X-rays, each used for specific diagnostic purposes. Your dentist will recommend the appropriate type of X-ray based on your age, dental health history, and any symptoms or concerns you may have.
- Bitewing X-Rays
Bitewing X-rays are commonly used to detect cavities between teeth, particularly in the areas that are hard to see visually. They involve biting down on a small film or sensor while the X-ray machine captures images of the upper and lower teeth simultaneously. Bitewings are often taken during routine check-ups and can also reveal early signs of bone loss associated with gum disease.
- Periapical X-Rays
Periapical X-rays focus on one or two teeth and capture the entire tooth structure, from the crown to the root and the surrounding bone. These X-rays are used to examine specific areas of concern, such as an infection at the tooth’s root or a suspected abscess. Periapical X-rays provide detailed images, which are invaluable in diagnosing problems deep within the tooth.
- Panoramic X-Rays
Panoramic X-rays capture the entire mouth in a single image, including the upper and lower jaws, teeth, sinuses, and surrounding bone. This type of X-ray is often used for initial assessments, orthodontic evaluations, and planning major dental treatments such as implants or extractions. Panoramic X-rays are also helpful in detecting impacted wisdom teeth and abnormalities in the jawbone.
- Occlusal X-Rays
Occlusal X-rays show the floor of the mouth and are used primarily to examine the alignment of the teeth and jaw in children. These X-rays can reveal issues with tooth development and the position of permanent teeth as they come in.
- Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
CBCT, or dental CT scans, produce 3D images of the teeth, jawbone, nerves, and soft tissues. While not commonly used for routine check-ups, CBCT scans are invaluable for planning complex procedures like dental implants and detecting abnormalities in the jaw structure. CBCT scans offer more detailed images than traditional X-rays and allow for precise treatment planning.
The Benefits of Regular Dental X-Rays
While dental X-rays are often used to diagnose specific problems, they also provide numerous benefits as part of a preventive dental care plan. Here are some of the key benefits of undergoing regular dental X-rays:
Early Diagnosis of Dental Problems
X-rays help detect dental issues at an early stage when they’re easier and less expensive to treat. Early diagnosis can prevent issues like cavities, gum disease, and infections from worsening, saving patients time, money, and discomfort.
Customized Treatment Planning
X-rays allow dentists to create customized treatment plans based on a detailed view of the patient’s oral structure. Whether planning a filling, root canal, or dental implant, X-rays provide essential information to ensure successful and precise treatment outcomes.
Monitoring Dental Health Over Time
For patients with ongoing dental issues, X-rays are invaluable for monitoring progress and tracking changes in oral health over time. Regular X-rays can help dentists assess how well a treatment is working or identify potential problems before they escalate.
Enhanced Patient Education
X-rays give patients a visual understanding of their dental issues, making it easier for dentists to explain treatment options. When patients can see the exact problem on an X-ray image, they are often more motivated to follow through with recommended treatments.
Are Dental X-Rays Safe?
One common concern among patients is the safety of dental X-rays, especially regarding radiation exposure. While X-rays do involve exposure to radiation, the levels are minimal and considered safe for most patients. Modern dental practices use digital X-rays, which emit significantly less radiation than traditional film X-rays. Digital X-rays also provide faster results and are more environmentally friendly.
For added protection, dentists use lead aprons and thyroid collars to shield sensitive areas from radiation. Furthermore, dentists are careful to limit the frequency of X-rays, taking them only when necessary and based on individual needs.
Exceptions and Precautions
While dental X-rays are safe for most people, certain populations may require additional precautions:
- Pregnant Women: X-rays are typically postponed for pregnant women unless absolutely necessary. If an X-ray is required, the dentist will take extra measures to protect both the mother and fetus.
- Young Children: For children, dentists are cautious about minimizing radiation exposure. X-rays for children are typically only done when needed for monitoring tooth development or addressing specific concerns.
- Patients with High Radiation Exposure: People who are frequently exposed to radiation in other settings, such as certain occupations, may discuss alternative diagnostic methods or longer intervals between X-rays with their dentist.
How Often Should You Get Dental X-Rays?
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on a variety of factors, including age, dental health history, and current oral health status. Here’s a general guideline for how often you might need X-rays:
- For New Patients: If you’re visiting a new dentist for the first time, they may take X-rays to get a complete picture of your oral health.
- Routine Check-Ups (Adults): For adults with healthy teeth and gums, bitewing X-rays are usually recommended every 1-2 years. Panoramic or other types of X-rays may be taken less frequently, depending on individual needs.
- Routine Check-Ups (Children): Children and teens may require X-rays more frequently to monitor tooth development and eruption patterns.
- For Patients with Dental Issues: Patients with a history of cavities, gum disease, or other dental problems may need more frequent X-rays to monitor their condition and ensure successful treatment outcomes.
Your dentist will evaluate your specific situation and determine an appropriate schedule for X-rays.
The Future of Dental X-Ray Technology
As technology advances, the field of dental imaging continues to improve. Here are a few exciting developments that are shaping the future of dental diagnostics:
- Lower Radiation Digital X-Rays: Newer digital X-ray machines continue to reduce radiation exposure, making them even safer for patients.
- 3D Imaging and Cone Beam Technology: 3D imaging provides more comprehensive views of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues, making it an invaluable tool for complex procedures.
- AI-Assisted X-Ray Interpretation: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into dental diagnostics to assist in reading X-rays, potentially increasing accuracy and efficiency in identifying dental problems.
These technological advancements make dental X-rays safer and more precise, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays are a fundamental tool in diagnosing, preventing, and treating a wide array of oral health issues. They provide essential insights that can’t be obtained through a visual exam alone, enabling early detection and personalized treatment plans. While some patients may worry about the safety of X-rays, modern technology has made them extremely safe, with minimal radiation exposure. Regular dental X-rays, based on your dentist’s recommendations, play a critical role in maintaining optimal oral health.
Understanding the importance of X-rays in dental diagnostics empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care. With the right balance of routine exams, X-rays, and preventive care, you can achieve and maintain a healthy, confident smile for years to come.